2307. The sum
A sequence of
n integers is given. You must
answer range-sum queries on this array.
Input. The first line
contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 0 ≤ k ≤ 105) – the number of
elements in the array and the number of queries.
Each of the following k lines contains one query of the
following types:
·
A l r x – assign the value x to every element with indices from l to r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n, 0 ≤ x ≤ 109)
·
Q l r – find the sum of array
elements with indices from l to r (1 ≤ l ≤ r
≤ n)
Initially, the array is filled
with zeros.
Output. For each query of
the form Q l r, print the sum of
numbers on the corresponding segment.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
5 9 A 2 3 2 A 3 5 1 A 4 5 2 Q 1 3 Q 2 2 Q 3 4 Q 4 5 Q 5 5 Q
1 5 |
3 2 3 4 2 7 |
SOLUTION
data
structures – segment tree
Algorithm
analysis
To solve the problem, it is necessary to
implement a segment tree that supports range operations – assignment and
summation.
In each node of the tree, the variable add stores the value assigned to all elements of the
segment corresponding to that node. If a node represents the segment [l; r],
then the sum of the elements on this segment is equal to add * (r – l + 1).
When performing assignment and summation
operations, while descending the tree from the root to the leaves, the value of
add in each node must be pushed down to the
next level of the tree.
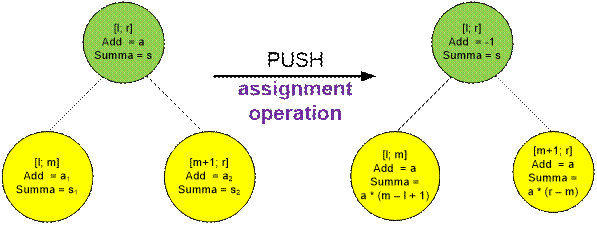
When an assignment operation is performed,
the previous sum values in the child nodes s1 and s2,
as well as the pending assignment values a1 and a2,
are discarded.
During the construction of the segment
tree, the variable add in each node is initialized with a value that
will never be assigned to the elements of any segment (for example, -1).
Algorithm
implementation
The segment tree is stored as an array SegTree,
whose elements are of type node. Each node of the tree corresponds to a
certain segment of the array and stores information about that segment.
The node structure contains two
fields:
·
sum – the sum of the elements on the
corresponding segment;
·
add – the value of the pending assignment
(lazy propagation).
The constructor is called automatically
when each node of the tree is created:
·
sum is initialized to zero, since at the
construction stage the node does not yet contain any accumulated information
about element values;
·
add is initialized to -1, which is used as a
special marker indicating the absence of a pending assignment. It is assumed
that this value will never be actually assigned to elements of the array.
struct node
{
long long sum, add;
node() : sum(0), add(-1) {}
};
vector<node> SegTree;
The function Push
propagates the value add from node v to its child nodes. If add ≠ -1, this value must be pushed
down one level in the tree. After the propagation is completed, the value of add in node v is set to -1.
void Push(int v, int lpos, int mid, int rpos)
{
If add = -1, then there is no
pending operation in node v.
if (SegTree[v].add == -1) return;
Recompute the values of add and sum in the child nodes of
node v.
SegTree[2*v].add = SegTree[v].add;
SegTree[2*v].sum = (mid - lpos + 1) * SegTree[v].add;
SegTree[2*v+1].add = SegTree[v].add;
SegTree[2*v+1].sum = (rpos - mid) * SegTree[v].add;
After the propagation is completed, set add = -1 in node v.
SegTree[v].add = -1;
}
The function SetValue assigns the value val to all
elements in the segment [left; right]. Node v corresponds to the segment [lpos;
rpos].
void SetValue(int v, int lpos, int rpos, int left, int right, int val)
{
if (left > right) return;
If the segment [left; right] corresponds to the segment [lpos;
rpos] stored in the tree node, then we assign the
appropriate values to the variables add and sum in this node.
if ((lpos == left) && (rpos == right))
{
SegTree[v].add = val;
SegTree[v].sum = (long long)(right - left + 1) * val;
return;
}
Find
the midpoint of the segment: mid = (lpos + rpos)
/ 2.
int mid = (lpos + rpos) / 2;
Perform
propagation if add is not equal to -1.
Push(v, lpos, mid, rpos);
Recursively process the left and right child nodes of the current segment
tree node.
SetValue(2*v, lpos, mid, left, min(mid, right), val);
SetValue(2*v+1, mid+1, rpos, max(left, mid+1), right, val);
Recompute the sum value in node v using the sum values of its
children.
SegTree[v].sum = SegTree[2*v].sum + SegTree[2*v+1].sum;
}
The
function Summa returns the sum of the elements in the segment [left; right].
Node v
corresponds to the segment [lpos; rpos].
long long Summa(int v, int lpos, int rpos, int left, int right)
{
if (left > right) return 0;
If the segment [left; right] coincides with the segment [lpos;
rpos] stored in node v of the tree, return the sum
value stored in this node.
if ((lpos == left) && (rpos == right))
return SegTree[v].sum;
Find
the midpoint of the segment: mid = (lpos + rpos)
/ 2.
int mid = (lpos + rpos) / 2;
Perform
propagation if add is not equal to
-1.
Push(v, lpos, mid, rpos);
Split the
segment [lpos; rpos] into two subsegments: [lpos;
mid] and [mid + 1; rpos]. Recursively
compute the sums on these subsegments and add the obtained values.
return Summa(2*v, lpos, mid, left, min(mid, right)) +
Summa(2*v+1, mid+1, rpos, max(left, mid+1), right);
}
The main part of the program. Read the
input data and initialize the segment tree.
cin >> n >> k;
SegTree.resize(4 * n);
Process k queries. Depending on the
type of query, we either perform a range assignment or compute the sum over the
specified segment.
while (k--)
{
cin >> c;
if (c == 'A')
{
cin >> l >> r >> x;
SetValue(1, 1, n, l, r, x);
}
else
{
cin >> l >> r;
cout << Summa(1, 1, n, l, r) << endl;
}
}
Algorithm analysis –
class
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class SegmentTree
{
public:
const static int NONE_ASSIGN =
-1;
vector<long long> Summa, Add;
int len;
SegmentTree(int n)
{
len = n;
Summa.resize(4*n);
Add.resize(4* n);
BuildZeroTree(1, 1, len);
}
void BuildZeroTree(int v, int lpos, int rpos)
{
if (lpos == rpos)
{
Summa[v] = 0;
Add[v] = NONE_ASSIGN;
}
else
{
int mid = (lpos + rpos) / 2;
BuildZeroTree(2*v, lpos, mid);
BuildZeroTree(2*v+1, mid + 1, rpos);
Summa[v] = Summa[2*v] + Summa[2*v+1];
Add[v] = NONE_ASSIGN;
}
}
void Push(int v, int lpos, int mid, int rpos)
{
if (Add[v] == NONE_ASSIGN) return;
Add[2*v] = Add[v];
Summa[2*v] = (mid - lpos + 1) * Add[v];
Add[2*v+1] = Add[v];
Summa[2*v+1] = (rpos - mid) * Add[v];
Add[v] = NONE_ASSIGN;
}
void SetValue(int left, int right, int val)
{
SetValue(1, 1, len, left, right, val);
}
void SetValue(int v, int lpos, int rpos,
int left, int right, int val)
{
if (left > right) return;
if ((lpos == left) && (rpos == right))
{
Add[v] = val;
Summa[v] = (long long)(right - left + 1) * val;
return;
}
int mid = (lpos + rpos) / 2;
Push(v, lpos, mid, rpos);
SetValue(2*v, lpos, mid, left, min(mid, right), val);
SetValue(2*v+1, mid+1, rpos, max(left, mid + 1), right, val);
Summa[v] = Summa[2*v] + Summa[2*v+1];
}
long long Sum(int left, int right)
{
return Sum(1, 1, len, left, right);
}
long long Sum(int v, int lpos, int rpos, int left, int right)
{
if (left > right) return 0;
if ((lpos == left) && (rpos == right)) return Summa[v];
int mid = (lpos + rpos) / 2;
Push(v, lpos, mid, rpos);
return Sum(2*v, lpos, mid, left, min(mid, right)) +
Sum(2*v+1,
mid+1, rpos, max(left, mid + 1), right);
}
};
int n, k, l, r, x;
char c;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d\n", &n, &k);
SegmentTree s(n);
while (k--)
{
scanf("%c ", &c);
if (c == 'A')
{
scanf("%d %d %d\n", &l,
&r, &x);
s.SetValue(l, r, x);
}
else
{
scanf("%d %d\n", &l,
&r);
printf("%lld\n", s.Sum(l, r));
}
}
return 0;
}
Ðåàëèçàöèÿ äåðåâà
îòðåçêîâ íà óêàçàòåëÿõ
Èç ýëåìåíòîâ âåêòîðà v ôóíêöèÿ build ñîçäàåò äåðåâî îòðåçêîâ.
SegmentTree *build(vector<long long> &v, int
L, int R)
{
if (L == R)
{
SegmentTree *New = new SegmentTree ;
New->summa = v[L]; New->add = -1;
New->Left
= New->Right = NULL;
New->LeftPos = New->RightPos = L;
return New;
}
int m = (L + R) / 2;
SegmentTree *Left =
build(v,L,m);
SegmentTree *Right = build(v,m+1,R);
SegmentTree *Tree = new SegmentTree;
Tree->Left
= Left; Tree->Right = Right;
Tree->summa
= Left->summa + Right->summa;
Tree->LeftPos = Left->LeftPos;
Tree->RightPos = Right->RightPos;
Tree->add =
-1;
return Tree;
}
Ôóíêöèÿ SetValue ïðèñâàèâàåò çíà÷åíèå value âñåì ýëåìåíòàì íà îòðåçêå
[L; R].
void
SetValue(SegmentTree *&tree, int L, int R, long long
value)
{
if (L < tree->LeftPos)
L = tree->LeftPos;
if (R > tree->RightPos)
R = tree->RightPos;
if (L > R) return;
Åñëè [L; R] ñîîòâåòñòâóåò îòðåçêó, êîòîðûé õðàíèòñÿ â âåðøèíå äåðåâà [LeftPos; RightPos], òî ïðèñâàèâàåì
â òåêóùåé âåðøèíå äåðåâà ïåðåìåííûì add è summa ñîîòâåòñòâóþùèå çíà÷åíèÿ.
if ((tree->LeftPos == L)
&& (tree->RightPos == R))
{
tree->add
= value;
tree->summa = value * (R - L + 1);
return;
}
Åñëè çíà÷åíèå tree->add óñòàíîâëåíî
(íå ðàâíî -1), òî ñëåäóåò ïðîòîëêíóòü
åãî íà óðîâåíü
íèæå. Ïðè ýòîì ñëåäóåò ïåðåñ÷èòàòü
çíà÷åíèå ñóììû â äî÷åðíèõ âåðøèíàõ tree->Left->summa è tree->Right->summa.
if (tree->add != -1)
{
if (tree->Left != NULL)
tree->Left->add = tree->add,
tree->Left->summa = tree->add *
(tree->Left->RightPos - tree->Left->LeftPos
+ 1);
if (tree->Right != NULL)
tree->Right->add = tree->add,
tree->Right->summa = tree->add *
(tree->Right->RightPos - tree->Right->LeftPos
+ 1);
tree->add
= -1;
}
Ðåêóðñèâíî ìîäèôèöèðóåì ëåâîå
è ïðàâîå ïîääåðåâî. Ïåðåñ÷èòûâàåì çíà÷åíèå ñóììû â òåêóùåé âåðøèíå äåðåâà.
SetValue(tree->Left,L,R,value);
SetValue(tree->Right,L,R,value);
tree->summa
= tree->Left->summa + tree->Right->summa;
}
Ôóíêöèÿ Summa âîçâðàùàåò çíà÷åíèå ñóììû íà îòðåçêå
[L; R].
long long Summa(SegmentTree *&tree, int
L, int R)
{
if (L < tree->LeftPos)
L = tree->LeftPos;
if (R > tree->RightPos)
R = tree->RightPos;
if (L > R) return
0;
Åñëè [L; R] ñîîòâåòñòâóåò îòðåçêó â âåðøèíå äåðåâà, òî âîçâðàùàåì õðàíÿùååñÿ
â íåì çíà÷åíèå ñóììû.
if ((tree->LeftPos == L)
&& (tree->RightPos == R))
return tree->summa;
Ïðîèçâîäèì ïðîòàëêèâàíèå çíà÷åíèÿ add íà óðîâåíü íèæå ñ ïåðåñ÷åòîì ñóììû äëÿ äî÷åðíèõ óçëîâ.
if (tree->add != -1)
{
if (tree->Left != NULL)
tree->Left->add = tree->add,
tree->Left->summa = tree->add *
(tree->Left->RightPos - tree->Left->LeftPos
+ 1);
if (tree->Right != NULL)
tree->Right->add = tree->add,
tree->Right->summa = tree->add *
(tree->Right->RightPos - tree->Right->LeftPos
+ 1);
tree->add
= -1;
}
Âîçâðàùàåì èñêîìóþ ñóììó, èçâëåêàÿ èíôîðìàöèþ èç ëåâîãî è ïðàâîãî
ïîääåðåâà.
return Summa(tree->Left,L,R)
+ Summa(tree->Right,L,R);
}
Îñíîâíàÿ ÷àñòü ïðîãðàììû. Ñòðîèì äåðåâî îòðåçêîâ
Tree, ñîäåðæàùåå èçíà÷àëüíî
âñå íóëè.  çàâèñèìîñòè îò âõîäíîãî çàïðîñà ñîâåðøàåì ëèáî ãðóïïîâîå ïðèñâàèâàíèå, ëèáî âû÷èñëåíèå ñóììû íà îòðåçêå.
scanf("%d
%d\n",&n,&k);
Tree = build(v,0,n);
while(k--)
{
scanf("%c ",&c);
if (c == 'A')
{
scanf("%d %d %d\n",&l,&r,&x);
SetValue(Tree,l,r,x);
}
else
{
scanf("%d %d\n",&l,&r);
printf("%lld\n",Summa(Tree,l,r));
}
}